Kiran K
What is JSON Web Token?
JWT or JSON Web Token is an open standard that defines a compact and self-contained way for securely transmitting information between parties as a JSON object.
The main purpose of JWTs is to transfer claims between two parties.
The claims in a JWT are encoded as a JSON object that is digitally signed using JSON Web Signature (JWS) and/or encrypted using JSON Web Encryption (JWE).
JWS - Signatures are useful to validate the data against tampering.
JWT - Encryption is useful to protect the data from being read by third parties.
Signed JWTs have 3 different parts. These three elements are separated by dots.
-
Header
-
Payload
-
Signature
Header
The header typically consists of two parts: the type of the token, which is JWT, and the signing algorithm being used, such as HMAC SHA256 or RSA.

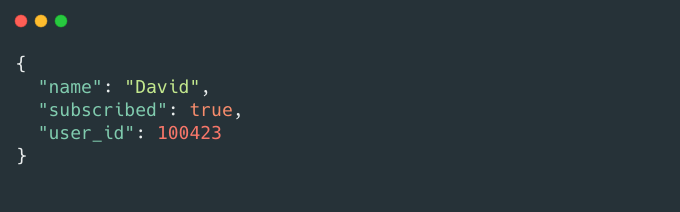
Payload
The second part of the token is the payload, which contains the claims. As a developer, you can include information about the user in the payload.
Signature
The signature will be created in the following way.

Final JWT
The output is three Base64-URL strings separated by dots.
[header].[payload].[signature]
